Technical specifications
The SGM DBE stationary suspended electromagnet is designed for the separation of ferrous material in waste and scrap processing, particularly when the iron content is relatively low.
The effectiveness of the DBE separator depends on several key factors:
- Size of ferrous components – The smaller the particles, the stronger the magnetic circuit required.
- Shape of the ferrous material – Spherical objects are more challenging to separate than elongated shapes.
- Burden depth of the material – The higher the material layer, the more complex the separation.
- Bulk density of the material – Higher density requires stronger magnetic performance.
- Moisture content – Wet materials complicate separation.
- Conveyor belt speed – Faster speeds make separation more demanding.
- Conveyor belt width – The separator must cover the entire width of the belt for effective ferrous recovery.
How It Works
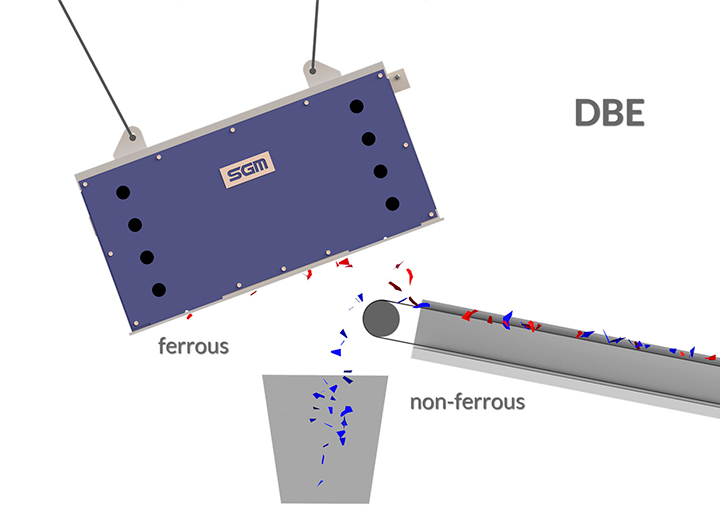
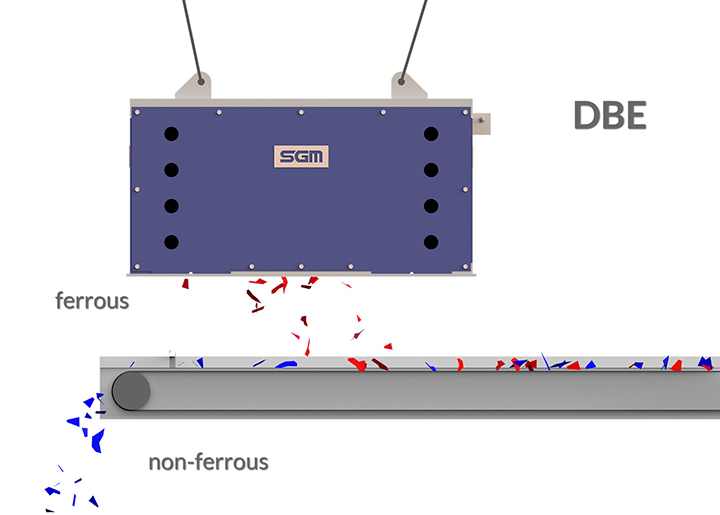
The DBE suspended magnet separator is fixed in position to attract ferrous metals from material conveyed beneath it. It is ideally positioned above the head pulley of the conveyor, where the material naturally opens as it leaves the belt, optimizing ferrous extraction. Alternatively, it can be installed along the conveyor’s length, depending on the specific application requirements.
Ferrous materials are lifted and held by the magnet, while non-magnetic materials follow their natural trajectory and continue along the conveyor for further processing.
DBE Models
SGM Magnetics offers 24 DBE models, each distinguished by:
- Power requirements
- Conveyor belt speed compatibility
- Electromagnet dimensions (length, width, height)


