Since the incineration of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) reduces its volume by 80% and weight by 90%, it is becoming an increasingly common alternative to landfilling.
Bottom ash is the incombustible residue left after Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) incineration. Globally, over 600 Waste-to-Energy (WtE) plants process approximately 130 million tonnes of waste annually, generating an estimated 19.5 to 26 million tonnes of bottom ash each year. These residues contain significant amounts of recoverable metals and minerals, offering substantial opportunities for material recovery and recycling.
Efficient bottom ash processing not only reduces landfill dependency but also enhances resource recovery, supporting a more sustainable and circular economy.
SGM provides advanced separation technologies to maximize metal extraction and ensure high-purity material recovery, helping industries turn waste into valuable resources.
Bottom Ash Treatment: A Valuable Resource for Recycling
Incinerator ash composition and recovery potential
The ash produced by incinerators consists of fly ash and bottom ash (Incinerator Bottom Ash, IBA), which can be either combined at the exit of the incinerator (as in the USA) or kept separate.
IBA typically contains 1-3% valuable non-ferrous metals, including precious metals, and 5-12% ferrous content, making it a significant source for metal recovery. Additionally, up to 50% of IBA mass consists of particles smaller than 6 mm, depending on moisture levels, requiring specialized separation technologies and expertise to ensure efficient material recovery.
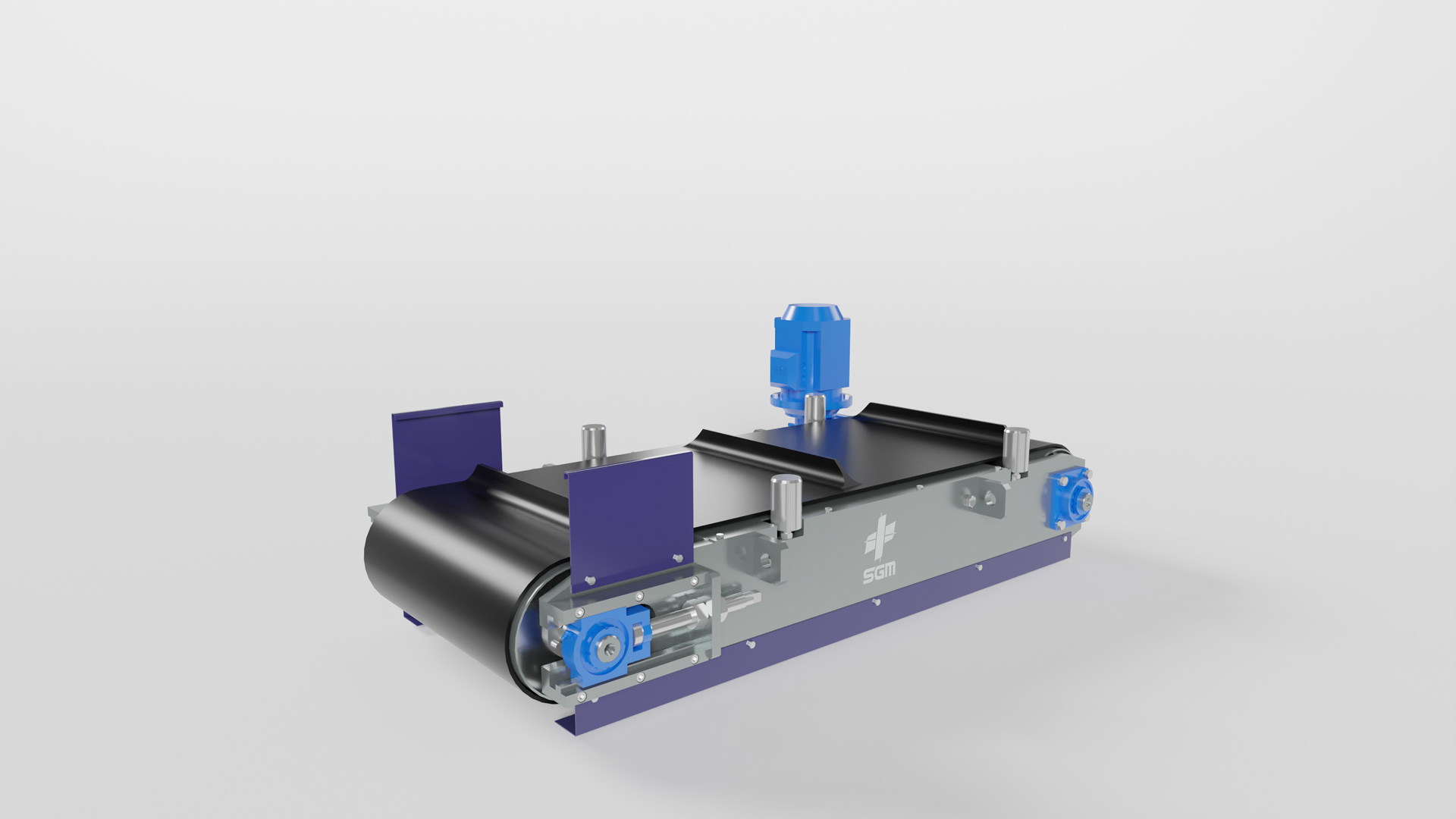
SGM provides tailored solutions for ash processing, utilizing advanced magnetic, eddy current, and sensor-based separation technologies to maximize metal recovery and optimize the reuse of incinerator residues.
SGM solutions for metal recovery from incinerator ash
With extensive experience and numerous global references, SGM has developed specialized solutions for processing MSW ash, including:
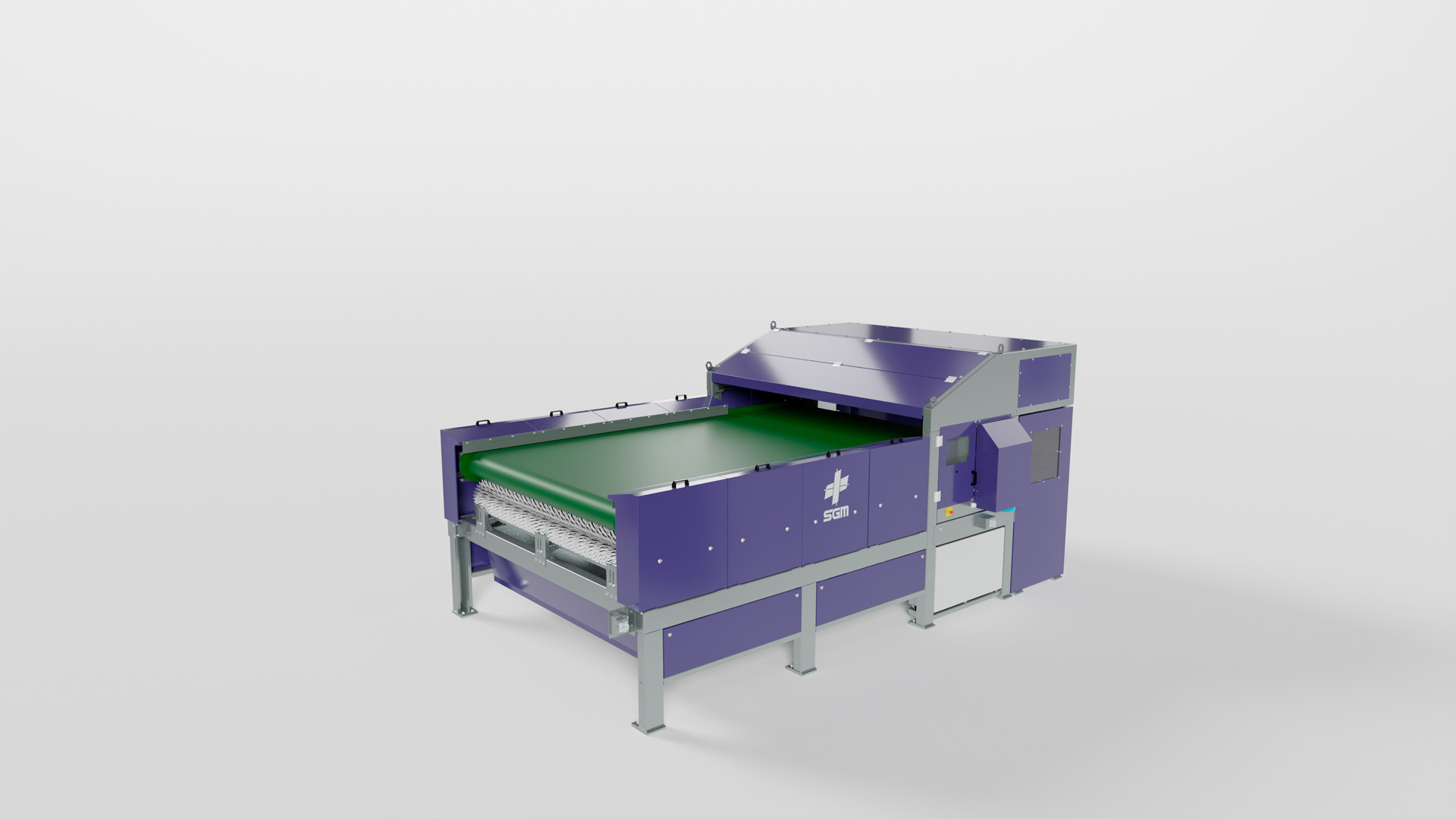
- Ballistic separators → For screening and concentrating solid pieces, including metals, while significantly reducing moisture content.
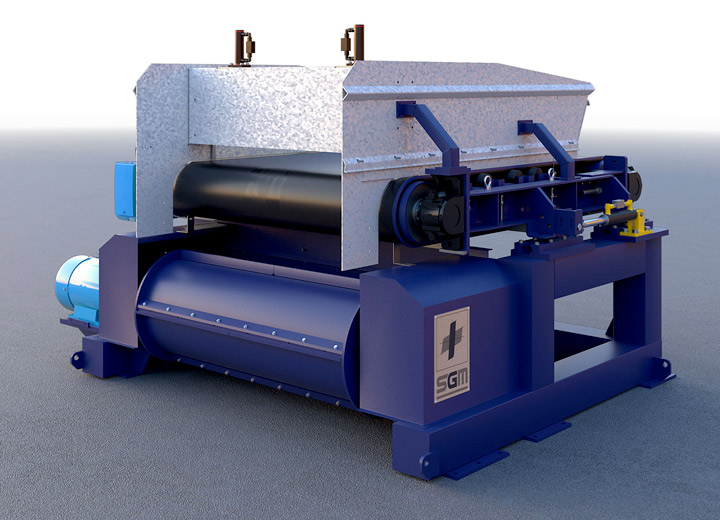
- High-frequency eddy current separators → Designed for recovering metals as fine as 0.2 mm.
- Sensor-based separators → For precise detection and separation of non-ferrous metals.
- Air gravity tables → For efficiently separating light fractions from heavy metals.
Decades of expertise, combined with the knowledge gained from group companies BSB Ambiente and Iris Ambiente (each processing 90,000 tonnes/year), allow SGM to deliver proven, high-performance solutions for incinerator ash treatment, helping industries optimize metal recovery and support a more sustainable circular economy.
Customers Who Trust Us